
On January 19, the US government hit its debt limit, triggering concerns over a possible payment default that could have disastrous consequences for the global economy. The US Congress had set the debt ceiling at $31.4 trillion in December 2021 which was breached last month. The ceiling is the statutory limit for borrowing by the US Treasury to fund federal expenses.
Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell has cleared that the central bank couldn’t protect the US economy from the possible damage caused by a debt ceiling standoff. Last week, Powell declined comment whether the Fed has started planning for a possible default by the US government.
United States government debt
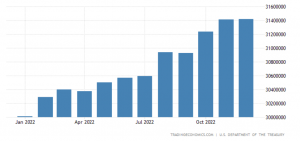
This is not the first time that the US government touching the debt limit — it has happened at least 20 times in the last two decades. The debt limit was revised 20 times since 2002 with the last instance in December 2021 when the Congress effected a $2.5 trillion increase. The current limit is around 125% of the US GDP.
The Covid-19 pandemic led to the ballooning of US debt as the US government rolled out economic stimulus packages worth around $5 trillion. This money was spent on pay-outs to households, small businesses, airlines, hospitals, schools and institutions to tide over the economic crisis triggered by the pandemic. The government also announced a number of tax cuts that led to a drop in revenues. All this led to the widening of fiscal deficit.
READ I The Great Indian House Trap: Burden of household work and labour force participation
Debt limit crisis is not a certainty
It is difficult to predict with certainty whether the US will face a debt crisis in the future. However, the US national debt has been increasing rapidly in recent years, and if this trend continues, it could potentially lead to a debt crisis. Factors such as economic growth, government spending, and interest rates will play a role in determining the likelihood of a debt crisis. It’s important to note that the government and the Federal Reserve have tools at their disposal to help manage the debt and avoid a crisis, but it will also depend on the willingness of politicians and the public to make tough choices about spending and taxes.
It is possible that Republicans may oppose efforts by the Biden administration to raise the debt limit. Historically, raising the debt limit has been a contentious issue, with both parties taking different positions on the matter. Republicans have traditionally been more fiscally conservative and may be less likely to support increasing the debt limit without significant spending cuts or other fiscal reforms.
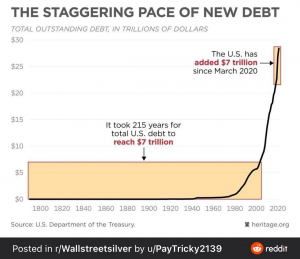
However, the specific actions that the Biden administration takes and the political climate at the time will play a large role in determining whether Republicans will block efforts to raise the debt limit. Ultimately, whether the Biden administration’s efforts to raise the debt limit are successful will depend on the actions and decisions of both the executive and legislative branches of government.
A debt crisis in the US could potentially have a significant impact on the global economy. The US economy is the largest in the world and a significant portion of global trade and investment is tied to it. If a debt crisis were to occur, it could lead to a sharp decline in economic growth and an increase in unemployment, which would likely have ripple effects throughout the global economy.
Additionally, a debt crisis in the US could lead to a loss of confidence in the US dollar, which could cause a decrease in its value and lead to inflation. It could also cause a disruption in the global financial markets, as many investors and financial institutions around the world hold US Treasury bonds.
However, it’s important to note that a US debt crisis is not a certain outcome, and the government and the Federal Reserve have tools at their disposal to help manage the debt and avoid a crisis. Additionally, other countries and international organizations also have tools to address an economic crisis and mitigate its impact on the global economy. It’s important to note that a debt crisis, if it happens, would not only be a problem for the US but for the whole world, as the US is a leading economy in the world and a debt crisis in the US would likely lead to a global economic crisis.
Options for Biden to tide over a crisis
If Republicans were to block the Biden administration’s efforts to raise the debt limit, the administration would have to find alternative ways to address the debt crisis. Some potential options include:
Negotiations and compromise: The Biden administration could attempt to negotiate with Republicans and reach a compromise on spending cuts or other fiscal reforms in exchange for their support in raising the debt limit.
Prioritising spending: The administration could prioritize spending on essential programs and services while cutting back on less important initiatives in order to reduce the deficit and avoid a debt crisis.
Using executive action: The president can use executive action to lower the debt limit and avoid a crisis.
Using the 14th amendment: The 14th amendment of the US Constitution provides that the validity of the public debt of the United States, authorized by law, shall not be questioned. It’s a constitutional tool that the president could use to bypass the congress and raise the debt limit if congress blocks it.
Using the Treasury’s emergency measures: The Treasury Department has emergency measures it can use to avoid defaulting on debt payments, such as redeeming securities held by government trust funds, temporarily suspending the sale of State and Local Government Series securities, and adjusting the terms of securities.
These options could have significant political and economic consequences, and the Biden administration would need to weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of each option before taking action. The options listed above are not exhaustive, and there might be other alternatives depending on the specific situation.
